A Comprehensive Guide to Launching n8n.io for Workflow Automation
In today’s fast-paced digital world, automation is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. n8n.io is an open-source workflow automation tool that enables you to automate repetitive tasks, integrate various services, and streamline your operations with minimal coding. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to get started with n8n, from understanding its benefits to launching and configuring your instance.
Fair-code workflow automation platform with native AI capabilities.
Combine visual building with
custom code, self-host or cloud, 400+ integrations.
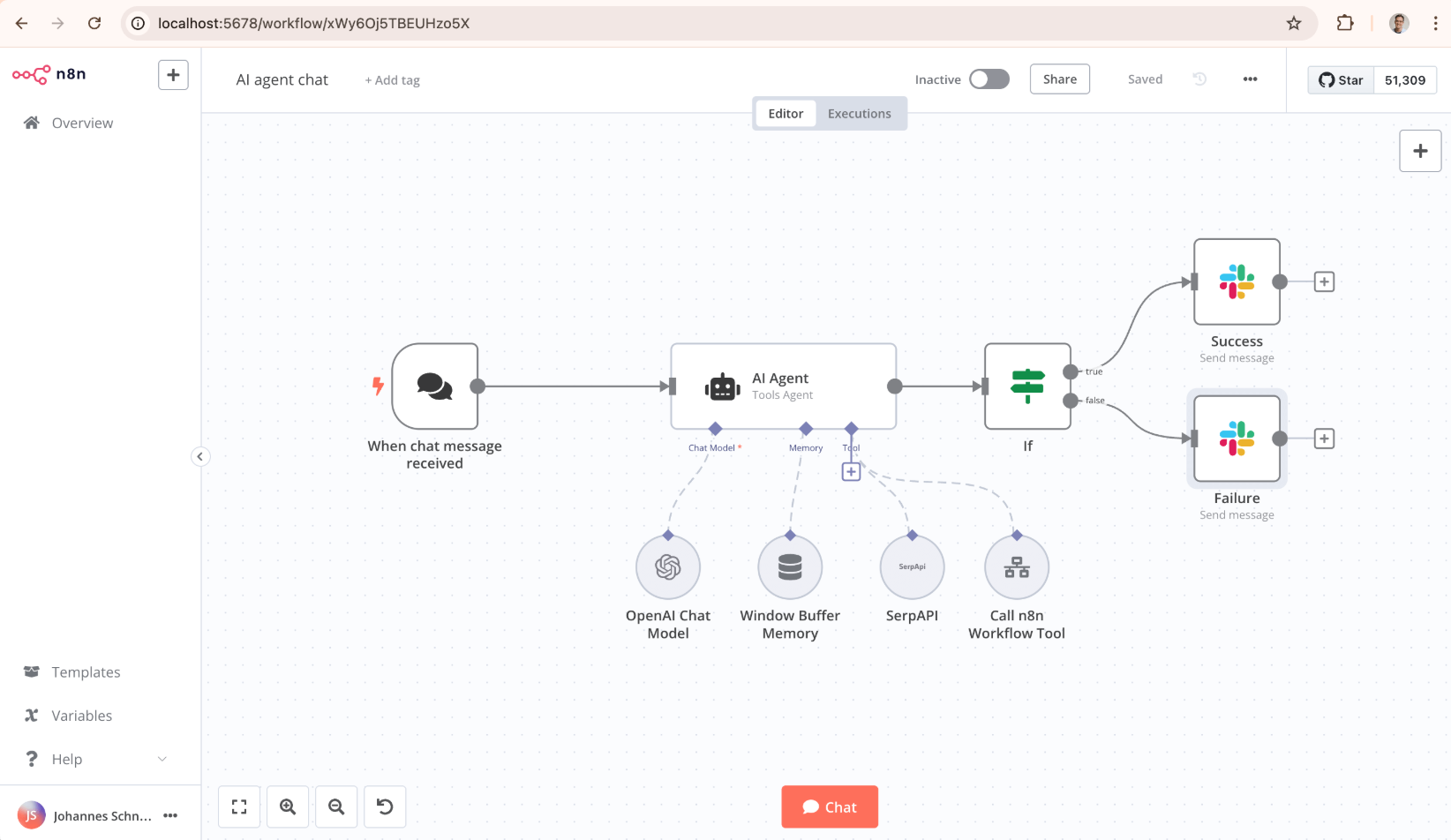
What is n8n?
n8n is a powerful, extendable workflow automation tool that allows users to create complex integrations between different applications without being constrained by proprietary platforms. It offers a visual interface where you can design workflows by connecting nodes representing various actions or triggers. Its open-source nature means you have full control over your data and can self-host your solution, making it ideal for businesses with specific security or compliance requirements.
Why Choose n8n?
-
Flexibility and Customization
Open Source:
With n8n, you get complete access to the source code, allowing you to customize workflows and integrate any service, regardless of whether it’s officially supported.
Self-Hosting:
Running n8n on your own infrastructure ensures that you control your data and comply with internal security policies.
Extensibility:
n8n’s modular architecture means you can easily extend its functionality by adding custom nodes or integrating new APIs.
-
Cost Efficiency
Free and Community-Driven:
n8n is free to use, and its active community continuously contributes plugins, integrations, and improvements.
No Vendor Lock-In:
Unlike many cloud-based solutions, n8n allows you to avoid being tied to a single vendor, giving you the freedom to scale and modify your workflows as needed.
-
Ease of Use
Visual Workflow Designer:
Its intuitive drag-and-drop interface simplifies the process of designing and managing automation flows.
Rich Ecosystem:
n8n supports a wide range of integrations, from popular cloud services to niche applications, reducing the need for custom API work.
Prerequisites for Launching n8n
Before you dive into the setup, ensure you have the following:
A Server or Local Environment: n8n can run on your local machine for testing or on a production server for live workflows. Docker (Recommended): For a streamlined and reproducible setup, using Docker is highly recommended. Node.js and npm: If you prefer a manual installation, ensure that you have Node.js (version 14 or higher) and npm installed. Basic Command Line Knowledge: Familiarity with terminal commands will help you navigate the installation and configuration process. SSL Certificate (for Production): If you plan to expose n8n to the internet, using an SSL certificate is crucial for securing communications.
Quick Start
Try n8n instantly with npx (requires Node.js):
npx n8n
Or deploy with Docker:
docker volume create n8n_data
docker run -it --rm --name n8n -p 5678:5678 -v n8n_data:/home/node/.n8n docker.n8n.io/n8nio/n8n
Resources
